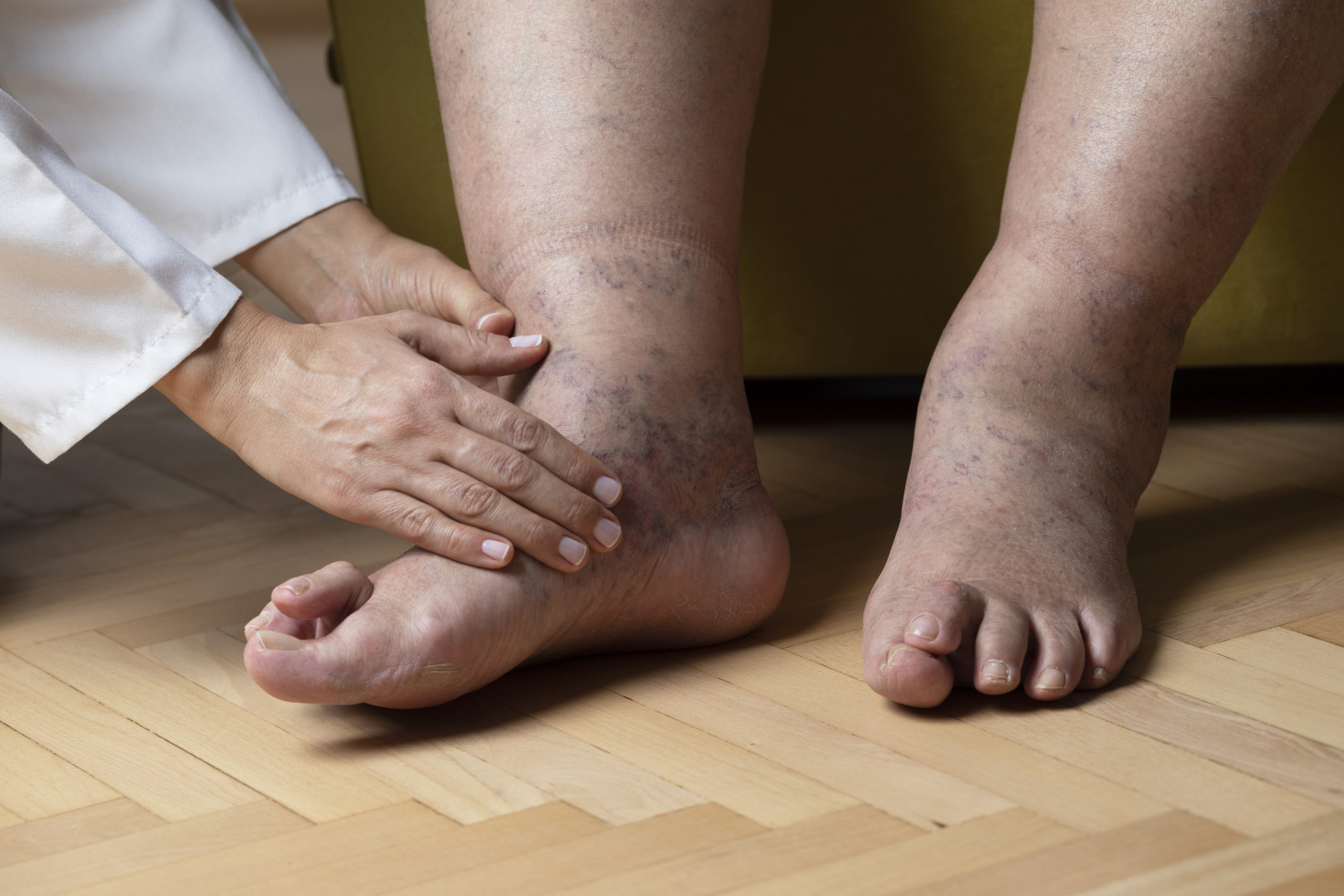
Peripheral neuropathy mainly affects the hands and feet, causing weakness, numbness, and discomfort. It can also affect other biological systems such as digestion, urine, and circulation. Damage to the nerves (peripheral nerves) outside the brain and spinal cord is the most common cause of peripheral Arlington neuropathy. The information from your spinal cord (central nervous system) and brain is sent to the rest of your body through the peripheral nervous system. Also, sensory information is sent to the central nervous system via peripheral nerves. Pain associated with peripheral neuropathy is often reported as tingling, burning, or stabbing. Symptoms often improve, especially if a curable disease causes them. Medication can help with peripheral neuropathy.
Understanding peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy arises when peripheral nerves are injured or destroyed and no longer function normally. The nerves’ natural function is disrupted as a result of this. They may send pain signals even if nothing is hurting you, or they may not produce a pain signal if something is hurting you. This might be because of:
- Injury.
- Illness that affects the entire body.
- Infection.
- Hormonal inconsistency.
- Various medications.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Hereditary condition.
As a result, the causes and kinds of the illness are diverse. There are more than 100 distinct kinds of peripheral neuropathy. Each type has its set of symptoms and treatment choices.
How to manage peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy symptoms may reduce or disappear with time, but in some cases, they never do. Here are some tips about how to know to live with it:
- Use pain relievers only as advised by your doctor. Most pain relievers function best when given before the discomfort becomes unbearable.
- Things that seem to aggravate it, such as hot or cold conditions and tight clothing or shoes, should be avoided.
- Allow yourself more time to complete tasks. If you are having trouble with a task, ask your buddies for assistance.
- Don’t consume alcoholic beverages. It has the potential to induce nerve damage on its own and exacerbate neuropathy.
- Keep track of your blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause nerve injury.
- Exercise extreme caution when utilizing knives, scissors, or other sharp instruments.
- When cleaning, working outside, or doing repairs, wear gloves to protect your hands.
- Sit down whenever you need to, even if you are cleaning your teeth or preparing a meal.
Damage to one or more sets of nerves causes peripheral neuropathy. The impact on your body is determined by which nerve groups are not functioning properly. An accident, a systemic ailment, or drugs might all be factors. You can postpone the onset of neuropathy or prevent it from worsening by addressing the underlying cause. Self-care practices such as daily planning can assist you in managing your illness and improving your quality of life.
Get medical attention immediately if you detect unusual tingling, weakness, or pain in your hands or feet. The greatest chance for treating your symptoms and preventing future damage to your peripheral nerves is to get a diagnosis and therapy right away. Call Interventional Pain and Regenerative Medicine Specialists or schedule a meeting online to learn more about peripheral neuropathy.