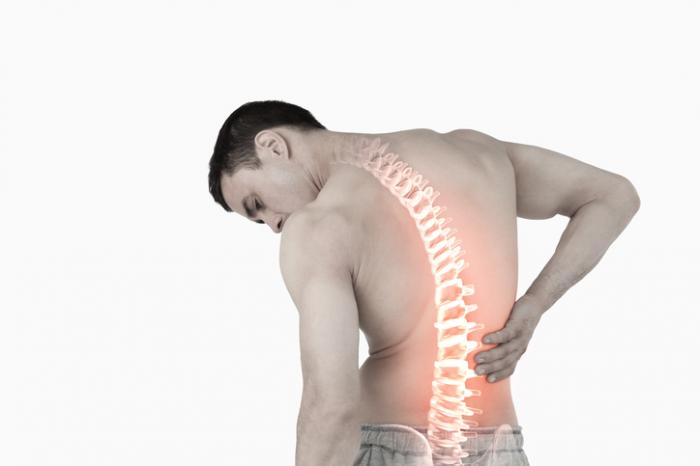
Back pain is a common complaint among older adults, but it can affect people of all ages. It is one of the main reasons people call in sick at work or miss school. Your back may feel sore due to muscle strain, spinal instability, and age-related conditions such as osteoporosis. The intensity of the discomfort also varies from mild, which can improve with home remedies, to severe pain that requires surgery. If you have had prolonged pain that is not improving for at least 3months, specialists at Link Neuroscience Institute recommend diagnosis to establish and treat the cause of your pain. Below are different conditions that can make your back sore.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis mainly occurs due to the wear and tear related to osteoarthritis. It is the narrowing of the spinal space which can result in nerve compression. The spinal area can become narrow anywhere along the spine, but it is common in the neck and back region. Spinal stenosis does not necessarily cause symptoms, but you may experience pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. If the symptoms are severe, your doctor may recommend surgery to create space for the
Degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease develops over time as your spinal discs wear and tear. The discs are rubbery cushions that separate the vertebrae and absorb impact or shock and have a tough membrane called the annulus that covers the soft inner materials. As you grow older, the disc annulus may develop cracks or tears due to the stress of everyday activities. If the tears occur close to the nerve, they produce pain. Sometimes the disc nucleus pushes out of the small openings and slips out of place. When it presses on nerves, you may experience symptoms such as tingling, numbness, and pain.
Herniated disc
A herniated disc refers to a disc along your spinal cord that slips out of place. Herniated discs are standard in older people due to degenerative discs. The annulus, the disc’s outer membrane, wears and tears as you age. As a result, the inner contents of the disc can push out through a weak area, pressing on nerves in the spinal space. Depending on where along the spine the disc bulges, you may experience pain, tingling, and loss of sensation in your arms or legs. Sometimes you may have a ruptured disc without the symptoms.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage covering the ends of bones wears out as you become older. It is a common form of arthritis that can affect any joint in the body, but it commonly attacks your spine, hips, knees, and hands. The gradual wear and tear of the cartilage eventually leads to friction between bones upon motion. When two bones rub against each other, they wear out, and as a natural response, the body forms bone spurs. Bone spurs make your joints rigid and affect your range of motion. The formation of bone spurs along your spine may cause narrowing of the spinal space, leading to nerve compression.
If your back pain is not responding to home remedies such as hot compresses and over-the-counter medication, book a session with your specialist at Link Neuroscience Institute for diagnosis and treatment to improve your quality of life.