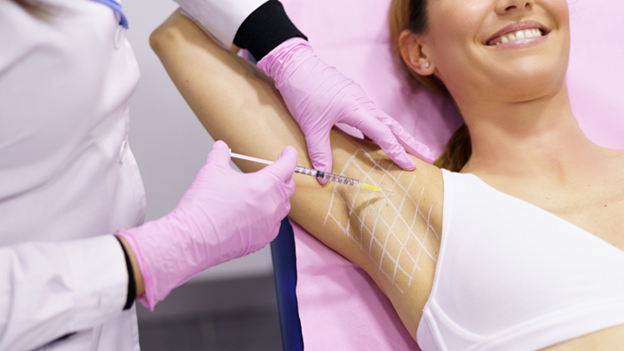
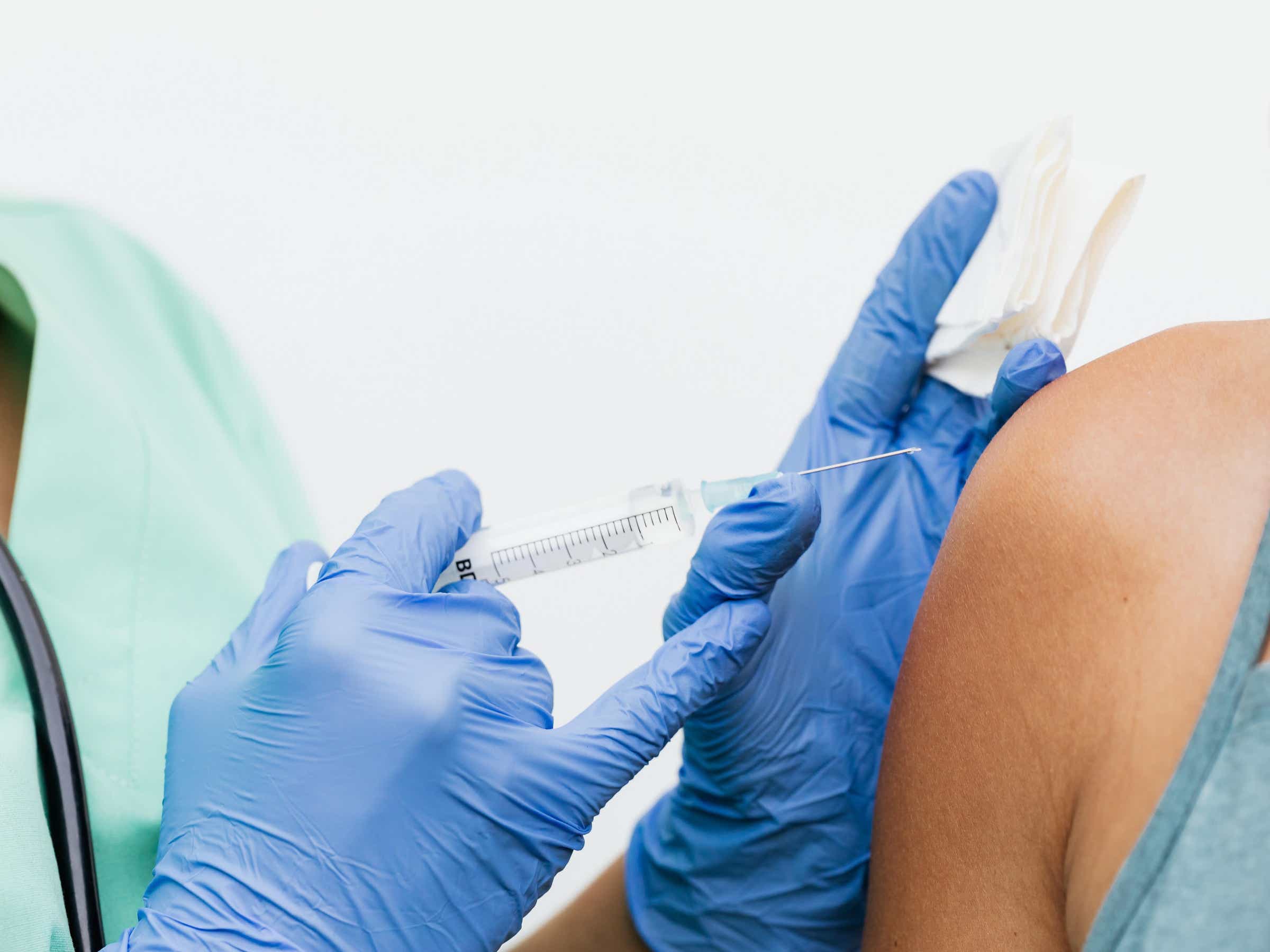
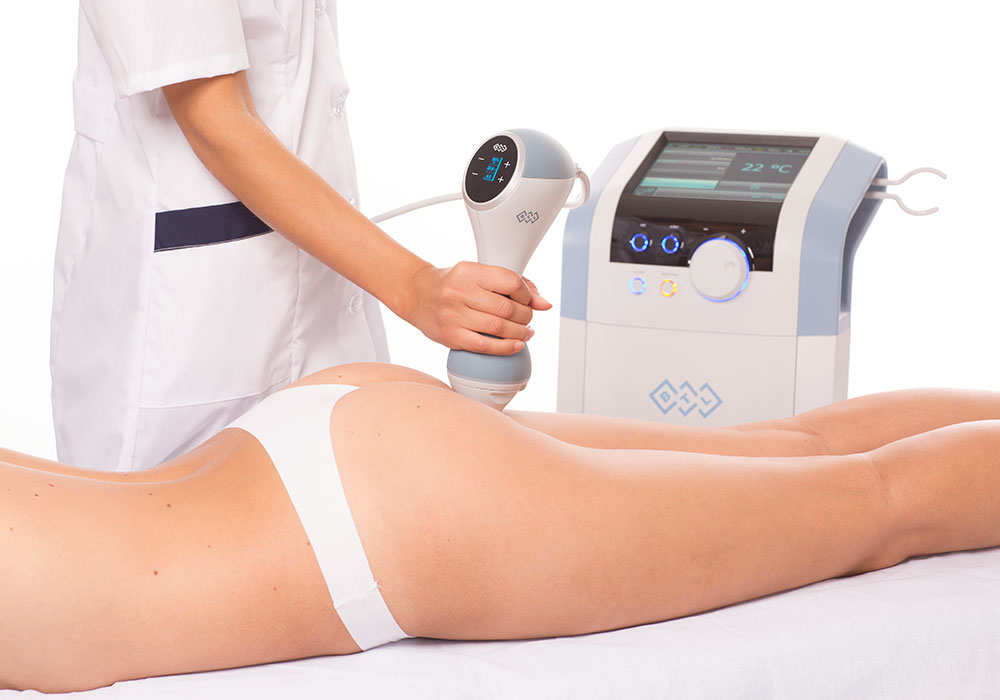
Excessive sweating is medically termed hyperhidrosis. It produces excessive perspiration in your body, sometimes for no apparent reason. Although it’s common, this condition may make one feel awkward or ashamed. A medical professional can assist in locating a symptom-management solution. It might consist of prescription drugs, therapies, or specific antiperspirants.
Types of hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is classified into two categories: primary or secondary hyperhidrosis.
- Primary or focal hyperhidrosis: It occurs in otherwise healthy individuals with no apparent cause and in certain areas of the body, usually the armpits, hands, feet, or face.
- Secondary or generalized hyperhidrosis: It is much less common and can be due to certain drugs, a variety of serious systemic diseases, neurological disorders, facial surgery, and anxiety.
What causes excessive sweating?
The majority of people who perspire excessively suffer from a disorder known as “idiopathic hyperhidrosis.” This indicates that the reason is not known. Even in the absence of heat or physical activity, the nerves responsible for producing sweat may become hyperactive and cause the sweat glands to release.
Hyperhidrosis of this kind frequently runs in families. If the person is anxious or stressed, it might get worse. The underarms are most likely to be affected, followed by the palms and feet, while the face is least likely to be affected.
Excessive sweating can be brought on by a medical condition for certain people. It’s crucial to visit the physician to undergo testing and rule out any medical conditions like:
- Diabetes
- Menopause
- Thyroid Problems
- Low Blood Sugar
- Some Types Of Cancer
- Heart Attack
- Nervous System Disorders
- Infections
Oversweating is another side effect of certain medications.
At-home hyperhidrosis treatment
At-home remedies for hyperhidrosis symptoms include using deodorant and antiperspirant. Sweat glands are sealed off by antiperspirants, causing the body to stop sweating. An aluminum-based deodorant is the best option for people with hyperhidrosis.
Bathing or taking showers more frequently also helps. Modest symptom relief may come from altering daily routine, such as taking more frequent showers.
Dressing in breathable materials also reduces excessive sweating. If you perspire a lot, wearing cotton or other breathable, more absorbent materials will make you feel more at ease. Polyester and blended materials tend to trap heat and increase perspiration. Avoid wearing them.
How is excessive sweating treated?
Depending on the area of the body afflicted, the severity of the diagnosis, and the best course of action, there are different ways to treat hyperhidrosis. The best treatments to help manage the symptoms can be found with the assistance of a dermatologist or healthcare provider. No single treatment is effective for every patient.
Most people who sweat excessively are unaware that they can receive assistance, but there are a few options available to them, and possible treatments include:
- Nonprescription antiperspirants: Because these home remedies are easily accessible, most patients start with them. When all other antiperspirants have failed, aluminum chloride-containing antiperspirants might work better. For patients, so-called “natural” deodorants are frequently ineffective. Antiperspirants with a prescription that contains hexahydrate aluminum chloride.
- Iontophoresis: It is a machine that drives ions into the sweat gland with a direct current and tap water that is periodically infused with aluminum ions or other materials.
- Oral drugs: belonging to the class of drugs called anticholinergics, which lessen perspiration.
- Topical medicated pads: Pads that are placed under the arms that are infused with anticholinergic drugs.
- Surgery: as a last resort, paraspinal sympathectomy, or blocking specific nerve pathways.
Hyperhidrosis medications
A healthcare provider or dermatologist may prescribe certain medicines to reduce the symptoms of hyperhidrosis, such as:
- Aluminium chloride gel
- Anticholinergic agents
- Beta-blockers.
- Medicated wipes.
Discuss the side effects of the abovementioned drugs before taking them.
Hyperhidrosis treatment therapies
In case medication and/or at-home treatment fail to alleviate symptoms, a physician might suggest more specialized therapies.
- Iontophoresis: It involves submerging your hands or feet in a small tub of running water. Sweat glands are gradually blocked by a low electrical current that is emitted through the water by a special device. It takes 10 to 20 minutes for each treatment. The person may require multiple treatments. The equipment may be covered by insurance, allowing one to complete the therapy at home.
- Injections of botulinum toxin (botox): Sweating production can be stopped for months at a time by injecting botulinum toxin into an overactive nerve. It is necessary to receive repeated treatments.
- Microwave therapy: The doctor applies a sophisticated tool to the skin’s afflicted area. The gadget permanently destroys sweat glands by emitting thermal energy, or heat. This procedure is performed in the office of a healthcare provider and lasts for one hour.
Hyperhidrosis surgery
When other treatments fail and the symptoms persist, the doctor may recommend surgery:
- Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS): An extremely minimally invasive procedure, an ETS involves a surgeon cutting a nerve in the body to stop the signal that causes your sweat glands to release perspiration.
- Sweat gland removal: A surgeon may use liposuction, laser, curettage, or cutting to remove your sweat glands.
If other treatments are ineffective for persistent sweating, surgery may be able to provide long-lasting benefits. Discuss potential surgical side effects with your surgeon to determine whether this procedure is apt or not.
Taking Care of Oneself
Preserving the cleanliness and dryness of the areas in question is crucial when one experiences excessive sweating. To prevent sweat from seeping through clothing, one should use absorbent pads.
A backup wardrobe should always be packed, and natural fabrics that let your skin breathe, like cotton or silk, are ideal. It’s important to consume lots of water to replenish fluids lost through perspiration. If the hands become sweaty, wearing gloves might make daily tasks easier for you. Remove the socks and shoes to allow the feet to breathe to reduce sweating.
Sweating ruins clothes is awkward, and can make social and professional interactions difficult. Sweating excessively can cause major practical problems, such as making it difficult to shake hands, grip a steering wheel, or hold tools. If left untreated, these issues could persist forever.